Ankylosing Spondylitis
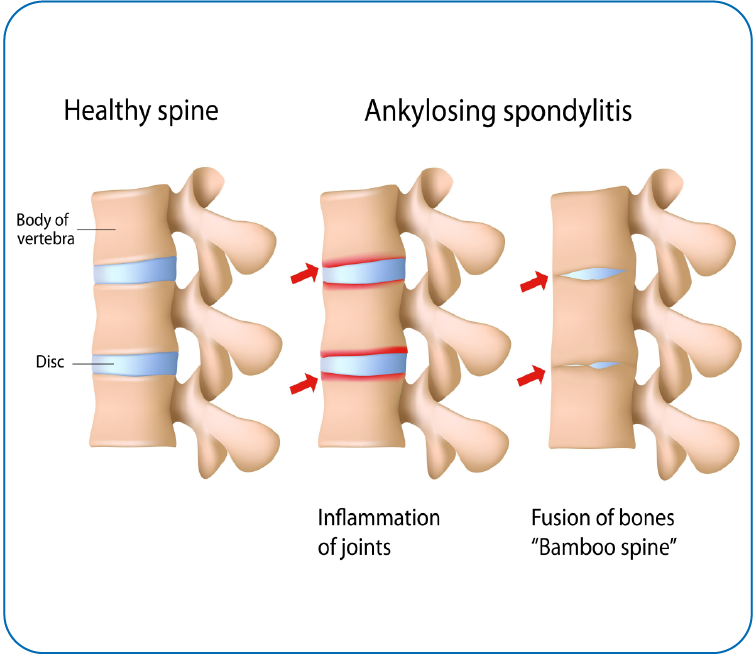
- Clinical criteria:
- Low back pain and stiffness for more than three months, which improves with exercise, but is not relieved by rest
- Limitation of motion of the lumbar spine in both the sagittal and frontal planes.
- Limitation of chest expansion relative to normal values correlated for age and sex
- Radiological criterion:
Sacroiliitis grade >2 bilaterally or grade 3-4 unilaterally
-Definite AS if the radiological criterion is associated with at least on clinical criterion.